
Unit Depreciation Expense = (Fair Value – Residual Value) / Useful Life in Units It is, obviously, most useful for depreciating production machinery. The method records a higher expense amount when production is high to match the equipment’s higher usage. Under the units-of-production method, the depreciation expense per unit produced is calculated by dividing the historical value of the asset minus the residual value by its useful life in terms of units (or the total number of products that it is expected to be able to manufacture). See how the declining balance method is used in our financial modeling course. In the first year, the depreciation expense is $40,000 ($100,000 * 2 / 5). They want to depreciate with the double-declining balance. The depreciation expense amount changes every year because the factor is multiplied with the previous period’s net book value of the asset, decreasing over time due to accumulated depreciation.įor example, Company A owns a vehicle worth $100,000, with a useful life of 5 years. Periodic Depreciation Expense = Beginning Value of Asset * Factor / Useful Life As it is a popular option with accelerated depreciation schedules, it is often referred to as the “double declining balance” method. To do so, the accountant picks a factor higher than one the factor can be 1.5, 2, or more.Ī 2x factor declining balance is known as a double-declining balance depreciation schedule. As the name implies, the depreciation expense declines over time. Declining balanceĪ declining balance depreciation is used when the asset depreciates faster in earlier years.
Expense definition free#
To learn more, check out our free accounting fundamentals course. The annual depreciation expense is $2,000,000, which is found by dividing $50,000,000 by 25. Periodic Depreciation Expense = (Fair Value – Residual Value) / Useful life of Assetįor example, Company A purchases a building for $50,000,000, to be used over 25 years, with no residual value. The method takes an equal depreciation expense each year over the useful life of the asset. The straight-line depreciation method is the most widely used and is also the easiest to calculate.
/operating-expenses-income-statement-592c83433df78cbe7ed46308.jpg)
Declining balance (accelerated depreciation).There are three common methods of calculating depreciation for a company: What are the Depreciation Expense Methods? For example, vehicles are assets that depreciate much faster in the first few years therefore, an accelerated depreciation method is often chosen.
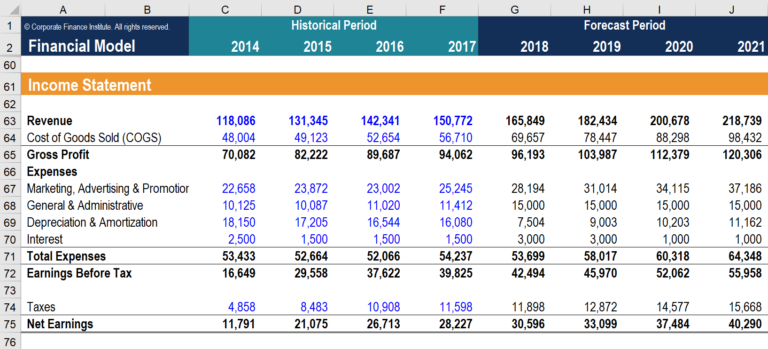
There are different methods used to calculate depreciation, and the type is generally selected to match the nature of the equipment.

To avoid doing so, depreciation is used to better match the expense of a long-term asset to periods it offers benefits or to the revenue it generates. Assuming the asset will be economically useful and generate returns beyond that initial accounting period, expensing it immediately would overstate the expense in that period and understate it in all future periods. When a long-term asset is purchased, it should be capitalized instead of being expensed in the accounting period it is purchased in. Updated FebruWhat is Depreciation Expense?


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
